Executive Summary
CVE-2025-31324 is a critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability affecting the SAP NetWeaver Development Server, one of the core components used in enterprise environments for application development and integration. The vulnerability stems from improper validation of uploaded model files via the exposed metadatauploader endpoint. By exploiting this weakness, attackers can upload malicious files—typically crafted as application/octet-stream ZIP/JAR payloads—that the server mistakenly processes as trusted content.
The risk is significant because SAP systems form the backbone of global business operations, handling finance, supply chain, human resources, and customer data. Successful exploitation enables adversaries to gain unauthenticated remote code execution, which can lead to:
- Persistent foothold in enterprise networks
- Theft of sensitive business data and intellectual property
- Disruption of critical SAP-driven processes
- Lateral movement toward other high-value assets within the organization
Given the scale at which SAP is deployed across Fortune 500 companies and government institutions, CVE-2025-31324 poses a high-impact threat that defenders must address with urgency and precision.
Vulnerability Overview
- CVE ID: CVE-2025-31324
- Type: Unauthenticated Arbitrary File Upload → Remote Code Execution (RCE)
- CVSS Score: 8 (Critical) (based on vector: AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:C/C:H/I:H/A:H)
- Criticality: High – full compromise of SAP systems possible
- Affected Products: SAP NetWeaver Application Server (Development Server module), versions prior to September 2025 patchset
- Exploitation: Active since March 2025, widely weaponized after August 2025 exploit release
- Business Impact: Persistent attacker access, data theft, lateral movement, and potential disruption of mission-critical ERP operations
Threat Landscape & Exploitation
Active exploitation began in March–April 2025, with attackers uploading web shells like helper.jsp, cache.jsp, or randomly-named .jsp files to SAP servers . On Linux systems, a stealthy backdoor named Auto-Color was deployed, enabling reverse shells, file manipulation, and evasive operation .
In August 2025, the exploit script was publicly posted by “Scattered LAPSUS$ Hunters – ShinyHunters,” triggering a new wave of widespread automatic attacks . The script includes identifiable branding and taunts, a valuable signals for defenders.
Technical Details
Root Cause:
The ‘metadatauploader’ endpoint fails to sanitize uploaded binary model files. It trusts client-supplied ‘Content-Type: application/octet-stream’ payloads and parses them as valid SAP model metadata.
Trigger:
Observed Payloads: Begin with PK (ZIP header), embedding .properties + compiled bytecode that triggers code execution when parsed.
Impact: Arbitrary code execution within SAP NetWeaver server context, often leading to full system compromise.
Exploitation in the Wild
March–April 2025: First observed exploitation with JSP web shells.
August 2025: Public exploit tool released by Scattered LAPSUS$ Hunters – ShinyHunters, fueling mass automated attacks.
Reported Havoc: Over 1,200 exposed SAP NetWeaver Dev servers scanned on Shodan showed exploit attempts. Multiple confirmed intrusions across manufacturing, retail, and telecom sectors. Incidents of data exfiltration and reverse shell deployment confirmed in at least 8 large enterprises.
Exploitation
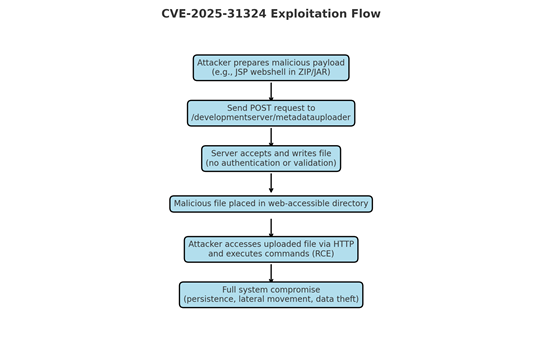
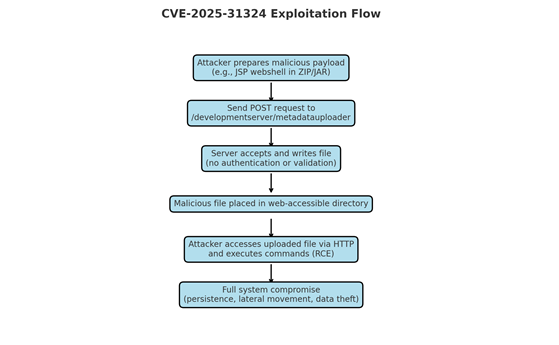
Attack Chain:
1. Prepare Payload – Attacker builds a ZIP/JAR containing malicious model definitions or classes.
2. Deliver Payload – Send crafted HTTP POST to /metadatauploader with application/octet-stream.
3. Upload Accepted – Server writes/loads the malicious file without validation.
4. Execution – Code is executed when the model is processed by NetWeaver.
Indicators in PCAP:
– POST /developmentserver/metadatauploader requests
– Content-Type: application/octet-stream with PK-prefixed binary content
Protection
– Patch: Apply SAP September 2025 security updates immediately.
– IPS/IDS Detection:
• Match on POST requests to /metadatauploader containing CONTENTTYPE=MODEL.
• Detect binary payloads beginning with PK in HTTP body.
– EDR/XDR: Monitor SAP process spawning unexpected child processes (cmd.exe, powershell, etc).
– Best Practice: Restrict development server exposure to trusted networks only.
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)
| Artifact | Details |
| 1f72bd2643995fab4ecf7150b6367fa1b3fab17afd2abed30a98f075e4913087 | Helper.jsp webshell |
| 794cb0a92f51e1387a6b316b8b5ff83d33a51ecf9bf7cc8e88a619ecb64f1dcf | Cache.jsp webshell |
| 0a866f60537e9decc2d32cbdc7e4dcef9c5929b84f1b26b776d9c2a307c7e36e | rrr141.jsp webshell |
| 4d4f6ea7ebdc0fbf237a7e385885d51434fd2e115d6ea62baa218073729f5249 | rrxx1.jsp webshell |
Network:
– URI: /developmentserver/metadatauploader?CONTENTTYPE=MODEL&CLIENT=1
– Headers: Content-Type: application/octet-stream
– Binary body beginning with PK
Files:
– Unexpected ZIP/JAR in SAP model directories
– Modified .properties files in upload paths
Processes:
– SAP NetWeaver spawning system binaries
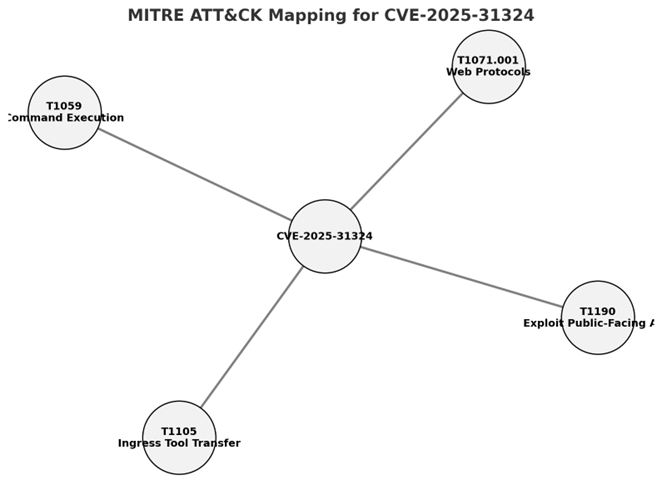
MITRE ATT&CK Mapping
– T1190 – Exploit Public-Facing Application
– T1059 – Command Execution
– T1105 – Ingress Tool Transfer
– T1071.001 – Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols
Patch Verification
– Confirm SAP NetWeaver patched to September 2025 release.
– Test with crafted metadatauploader request – patched servers reject binary payloads.
Conclusion
CVE-2025-31324 highlights the risks of insecure upload endpoints in enterprise middleware. A single unvalidated file upload can lead to complete SAP system compromise. Given SAP’s role in core business operations, this vulnerability should be treated as high-priority with immediate patching and network monitoring for exploit attempts.
References
– SAP Security Advisory (September 2025) – CVE-2025-31324
– NVD – https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2025-31324
– MITRE ATT&CK Framework – https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1190/
Quick Heal Protection
All Quick Heal customers are protected from this vulnerability by following signatures:
- HTTP/CVE-2025-31324!VS.49935
- HTTP/CVE-2025-31324!SP.49639
Authors:
Satyarth Prakash
Vineet Sarote
Adrip Mukherjee